Creating Renderworks styles
You can create a variety of custom Renderworks styles, in addition to the selection of basic styles that come with Vectorworks. Custom Renderworks styles can interpret textures, lighting, camera effects, and quality as needed for each specific rendering. See Renderworks styles for a general discussion of the rendering types and how to determine which type is most appropriate for particular models. Renderworks styles are saved as resources. For more information on creating resources, see Creating resources.
If you create a Renderworks style while the layer or viewport is rendered in any Renderworks mode or a Renderworks style, the current settings are used as the basis for the new style. This is a convenient way of saving render settings.
To create a Renderworks Style resource:
From the Resource Manager, click New Resource, select Renderworks Style, and then click Create. Alternatively, from the Resource Manager, select Renderworks Styles from the list of resource types on the tool bar, and click New Renderworks Style.
The Edit Renderworks Style dialog box opens.
Name the style resource, and select the style's type; for a photorealistic Renderworks style, see Choosing a photorealistic render type to help determine which option best meets your needs.
Different options to define the style are available depending on Type selected. See the appropriate section for the parameters:
Redshift by Maxon render style
The Renderworks style displays in the Resource Manager and is saved with the file. It is added to the list of available Renderworks styles in View > Renderworks Style, and in the Current Render Mode menu on the View bar.
To edit a Renderworks Style resource after it has been created, from the Resource Manager, right-click on the resource, and select Edit from the context menu. See Resource Manager: Resource viewer pane.
Realistic render style
A Realistic type creates a Renderworks style based on Custom Renderworks options. The preferences are grouped into several tabs of related parameters. Select each tab and specify the parameters.
Click to show/hide the parameters.Click to show/hide the parameters.
|
Parameter |
Description |
|
Options |
|
|
Anti-aliasing |
Select for smoother edges on objects and textures; deselect for faster rendering with rougher edges |
|
Shadows |
Renders shadows for a higher degree of realism |
|
Textures |
Renders the textures assigned to objects; deselect for faster rendering |
|
Blurriness |
Renders textures with blurred reflectivity and/or blurred transparency (this can add significant rendering time) |
|
Displacement mapping |
Renders with displacement mapping when a texture’s bump shader setting has a displacement height set; select the displacement mapping quality on the Quality tab. Deselect for faster rendering. |
|
Caustics |
Renders caustics from light objects that have Caustic Photons set to a value other than None from the Object Info palette (see Light source properties) |
|
Grass |
When a grass color shader is used for a texture, renders the blades of grass. When this option is deselected, the first shader color (or image) is used, but blades of grass are not rendered, saving rendering time for large surfaces or dense grass. |
|
Colors |
When selected, renders colors, and textures with colors; deselect to render colors as white |
|
Camera effects |
When selected, the Renderworks camera effects settings for the active camera are used in the rendering (see Placing a Renderworks camera). When deselected, only the active camera’s position and orientation settings are used in the rendering. Renderworks camera effects are camera-dependent; activate the camera to see the effects in the rendering. |
|
Fullscreen preview |
Immediately provides a full-screen preview at a very low resolution that is slow to resolve to final resolution; this is useful when working interactively to test rendering settings on a design layer. To save time, deselect this option when you are not making adjustments. Rendering occurs with final-rendered squares that populate the drawing. |
|
Quality |
For each parameter, select the quality level. Higher quality results in better resolution of rendered images, with better texture detail and softer shadows, but takes more time. |
|
Quality Levels |
Conveniently sets the quality level of all the options at one time. Custom indicates that some options have different quality levels set. |
|
Curved Geometry |
Select the quality level for faceting of curved geometry (such as NURBS surfaces) |
|
Anti-Aliasing |
Select the quality level for anti-aliasing (smoothing) of edges on objects and textures |
|
Indirect Lighting |
Select the quality level for indirect lighting effects |
|
Soft Shadows |
Sets the quality level of shadows for light objects that have Soft Shadows enabled. For area and line lights, specifies the sampling quality of the light. |
|
Blurriness |
Select the quality level of textures with blurry reflectivity and/or transparency |
|
Environment Lighting |
Select the sampling quality level for environment background lighting. This option has no effect when indirect lighting is enabled for the lighting options. |
|
Displacement Mapping |
When enabled on the Options tab and set for a bump shader, select the quality of the displacement mapping. Higher quality is more realistic for fine displacement bumps, but will require longer rendering times. Rendering can be significantly slower with displacement mapping. |
|
Max Reflections |
Enter the number of levels of reflection among shiny surfaces; a higher value slows rendering, but can yield a more realistic image for scenes with many inter-reflecting objects |
|
Lighting |
|
|
Apply lighting options |
Controls whether the Renderworks style changes the current lighting options when it is applied. Select the option to apply the style’s lighting options to the layer or viewport when the Renderworks style is applied. Deselect the option to leave the current lighting options unchanged when the Renderworks style is applied. |
|
Lighting Options |
Sets the lighting options; see Setting lighting options |
|
Edit Resource |
Opens the Edit Renderworks Background dialog box, to conveniently change background and environment lighting options that affect the rendering |
|
Edges |
|
|
Apply Artistic Edges |
Applies artistic edges on top of the realistic rendering |
|
Style |
Select an edge style |
|
Thickness (pixels) |
Specifies the edge thickness |
|
Color |
Specifies the edge color |
|
Background |
|
|
Apply Renderworks background |
Controls whether the Renderworks Background changes the current background options when it is applied. Select the option to apply the style’s background to the layer or viewport when the Renderworks style is applied. Deselect the option to leave the current background unchanged when the Renderworks style is applied. |
|
Renderworks Background |
Sets the Renderworks Background options; see Creating Renderworks backgrounds |
|
Environment Reflections |
Sets the background that reflects from glass and metal surfaces independently of the Renderworks Background that surrounds the drawn object; the resource should have either a Physical Sky or Panoramic Image background type. See Creating Renderworks backgrounds. |
Artistic render style
An Artistic type creates a Renderworks style based on Artistic Renderworks options. The preferences are grouped into two tabs of related parameters. Select each tab and specify the parameters.
Click to show/hide the parameters.Click to show/hide the parameters.
|
Parameter |
Description |
|
Artistic Style |
Select an Artistic Renderworks style and set any options |
|
Background |
|
|
Apply Renderworks background |
Controls whether the Renderworks Background changes the current background options when it is applied. Select the option to apply the style’s background to the layer or viewport when the Renderworks style is applied. Deselect the option to leave the current background unchanged when the Renderworks style is applied. |
|
Renderworks Background |
Sets the Renderworks Background options; see Creating Renderworks backgrounds |
Redshift by Maxon render style
A Redshift by Maxon type creates a Renderworks style based on Maxon's Redshift rendering technology, which can trace rays for reflections, lighting, volumetric effects, camera effects, and anti-aliasing. Images that do not use these effects may not benefit from using Redshift by Maxon. If enabled, rendering in design layers can interactively preview as you adjust views, textures, lighting, and geometry. If the computer hardware supports it, Redshift is processed on the GPU, so rendering time can be much shorter for complex files with many of these effects.
See www.vectorworks.net/sysreq for system requirements for processing Redshift on either the CPU or GPU. Computers that do not support Redshift will default to a Realistic type instead; when Redshift by Maxon is the selected Type, a sentence above the tabs indicates whether the machine supports Redshift. If you have access to Vectorworks Service Select benefits, Redshift by Maxon style renderings can be processed on Vectorworks Cloud Services.
The preferences are grouped into several tabs of related parameters. Select each tab and specify the parameters.
Click to show/hide the parameters.Click to show/hide the parameters.
|
Parameter |
Description |
|
Options |
|
|
Update Mode |
Select Bucket or Progressive update mode in Redshift: Bucket: updates the image with square tiles or "buckets" in an inside-out pattern. With this mode, rendering time is extended but rendering quality is improved. Progressive: immediately provides a full-screen preview at a very low resolution that is slow to resolve to final resolution; this is useful when working interactively to test rendering settings on a design layer. Final rendering quality depends on the number of progressive passes. |
|
Progressive Passes |
Select the number of passes to display. More passes result in a higher final quality, but take longer to complete. |
|
Enable interactive preview rendering (IPR) in design layers |
Enables Progressive Update Mode to work interactively within a design layer as you edit the drawing in a 3D view. IPR's initial preparation can take several seconds before generating the first rendering, depending on the complexity of the model and the computer's hardware capabilities. The interactive progressive rendering becomes faster after the initial rendering. Actions such as changing the view (panning, zooming, flyover) and changing existing lights, update the preview very quickly. Some actions, such as adding or deleting an object, applying a new background, or changing textures, slow the preview's reaction time. Other actions, such as changing render modes, changing geometry quality settings, and turning camera effects on and off, require IPR to repeat the initial preparation step before re-rendering. IPR settings, including the starting and ending resolutions, only affect design layer rendering; they have no effect on the rendering of a sheet layer, viewport, exported image, print, and so on. |
|
Starting Resolution |
Set the initial rendering resolution for Redshift IPR; a lesser resolution creates a faster initial preview, at a lower quality, that improves as the progressive passes are completed |
|
Ending Resolution |
Set the final rendering resolution for Redshift IPR on the design layer; a lesser resolution completes the rendering faster, but at a lower final quality |
|
Enable denoising |
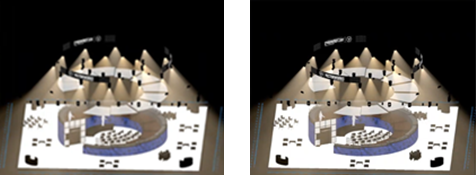
Uses artificial intelligence to replace speckled rendering artifacts with smooth continuous shading. For some scenes, setting Sampling lower on the Quality tab and using denoising can result in a similar final quality rendering with shorter processing time than a higher quality without denoising. Disable denoising for faster rendering of large models on slower computers, especially when using interactive preview rendering in design layers.
The image on the left uses Very High Sampling with Enable denoising turned off; its render time was 6:01. The image on the right uses Low Sampling with Enable denoising turned on; its render time was 1:31. |
|
Render shadows |
Renders shadows for a higher degree of realism |
|
Show textures |
Renders the textures assigned to objects; deselect for faster rendering |
|
Show colors |
When selected, renders colors, and textures with colors; deselect to render colors as white |
|
Enable camera effects |
When selected, the Renderworks camera effects settings for the active camera are used in the rendering (see Placing a Renderworks camera). When deselected, only the active camera's position and orientation settings are used in the rendering. Renderworks camera effects are camera-dependent; activate the camera to see the effects in the rendering. |
|
Quality |
|
|
Curved Geometry |
Select the quality level for faceting of curved geometry (such as NURBS surfaces) |
|
Sampling |
Select the sampling quality to affect anti-aliasing, blurred transparency and reflections, soft shadows, and indirect lighting quality; High creates a smoother, higher quality rendering, and Low results in faster rendering |
|
Lighting |
|
|
Apply lighting options |
Controls whether the Renderworks style changes the current lighting options when it is applied. Select the option to apply the style’s lighting options to the layer or viewport when the Renderworks style is applied. Deselect the option to leave the current lighting options unchanged when the Renderworks style is applied. |
|
Lighting Options |
Sets the lighting options; see Setting lighting options. For Redshift by Maxon render mode, you can use either environment lighting from a panoramic image background or ambient lighting. |
|
Background |
|
|
Apply Renderworks background |
Controls whether the Renderworks Background changes the current background options when it is applied. Select the option to apply the style’s background to the layer or viewport when the Renderworks style is applied. Deselect the option to leave the current background unchanged when the Renderworks style is applied. |
|
Renderworks Background |
Sets the Renderworks Background options; see Creating Renderworks backgrounds. Separate control of reflection backgrounds isn't possible with the Redshift render type. |